自动测试设备的预算-Automatic Test Equip
[09-13 17:05:13] 来源:http://www.88dzw.com 控制技术 阅读:8238次
文章摘要:The serial port provides even less power than the parallel port, and the voltage levels are not regulated. As mentioned above, these voltages can range from 3V to 30V and the signal polarity can be positive or negative. With the aid of some additional circuitry, the serial port can power a micropowe
自动测试设备的预算-Automatic Test Equip,标签:计算机控制技术,工厂电气控制技术,http://www.88dzw.comThe serial port provides even less power than the parallel port, and the voltage levels are not regulated. As mentioned above, these voltages can range from 3V to 30V and the signal polarity can be positive or negative. With the aid of some additional circuitry, the serial port can power a micropower circuit, but most applications require an external power supply.
When you use a serial port, sending and receiving data often requires a microcontroller. Some microcontrollers, such as the 68HC11, the 8051, and the PIC16C63, include a UART. Teamed with a MAX3320 RS-232 transceiver and a low-cost ceramic resonator, these microcontrollers can receive commands from a user-interface program running on the PC. Two options for this user interface are possible: using a text-only terminal program (for example, Hyperterminal or Procomm) or a custom graphical interface.
After receiving these commands from the user interface, the microprocessors shown in Figure 3 can perform relatively sophisticated control functions without the aid of the PC.
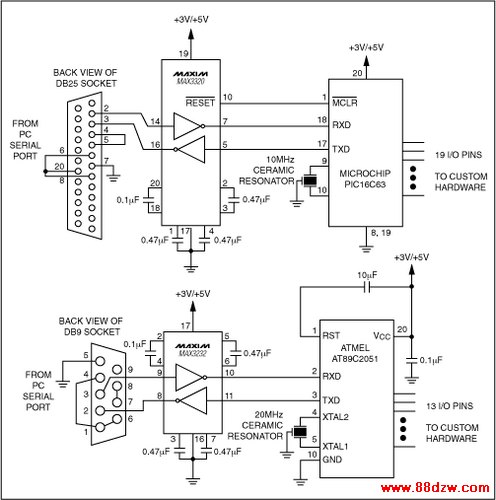
Figure 3. Having received commands from the PC via the serial bus, these microprocessors can perform relatively sophisticated control functions without the aid of the PC.
The IEEE-488 Bus
The IEEE-488 bus is a more complex, but far more versatile, system. It is also called the GPIB or HPIB bus. Unlike the serial and parallel ports, this bus can connect directly to more than one instrument at a time. In the test system shown in Figure 4, a PC controls an oven, a pressure source, a voltmeter, and a pressure-sensor tester. Control via one bus common to these various instruments and devices under test is possible using an IEEE-488 bus.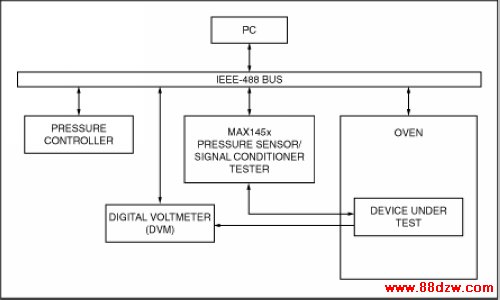
Figure 4. This test system permits automatic production testing and compensation of pressure sensors. The IEEE-488 bus facilitates communication between the PC and the components of the test system.
The IEEE-488 specification can allow multiple instruments to share the same bus, because the IEEE-488 bus uses a different output-driver structure than the serial and parallel ports discussed. Each IEEE-488 driver includes a strong pulldown resistor and a weak pullup, allowing one or more devices connected to the bus to pull each signal wire low (or to allow the line to remain high when none of the devices asserts a low).
Other advantages accompany the use of this bus. One such plus of the IEEE-488 interface is that it includes a hardware handshake that helps prevent data loss. Another significant advantage is its popularity among the major bench-top test equipment vendors (for example, HP/Agilent, Tektronix, Fluke, and Keithley). Because power supplies, relay switch banks, environmental chambers, oscilloscopes, digital voltmeters, function generators, and other equipment are available with IEEE-488 buses, you can automate virtually any bench-top test setup.
上一页 [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] 下一页
Tag:控制技术,计算机控制技术,工厂电气控制技术,控制技术
- 上一篇:场效应管的识别方法及好坏判断
《自动测试设备的预算-Automatic Test Equip》相关文章
- › 自动测试设备的预算-Automatic Test Equip
- › 基于多MCU的自动测试诊断系统的设计
- › 基于单片机控制的热源自动测试仪
- › 自动测试软件可靠性量化评估技术研究
- 在百度中搜索相关文章:自动测试设备的预算-Automatic Test Equip
- 在谷歌中搜索相关文章:自动测试设备的预算-Automatic Test Equip
- 在soso中搜索相关文章:自动测试设备的预算-Automatic Test Equip
- 在搜狗中搜索相关文章:自动测试设备的预算-Automatic Test Equip
分类导航
最新更新




 当前位置:
当前位置: