检测电路保持您的微处理器控制-Supervisory Cir
[09-13 17:05:09] 来源:http://www.88dzw.com 控制技术 阅读:8332次
文章摘要:Most of the earlier SOT devices are available in five or so standard threshold voltages. However, two of the four-terminal devices from Maxim (MAX6314 and MAX6315) represent the first in a growing line of supervisors that make available a wide range of custom thresholds and reset timeouts. The most
检测电路保持您的微处理器控制-Supervisory Cir,标签:计算机控制技术,工厂电气控制技术,http://www.88dzw.comMost of the earlier SOT devices are available in five or so standard threshold voltages. However, two of the four-terminal devices from Maxim (MAX6314 and MAX6315) represent the first in a growing line of supervisors that make available a wide range of custom thresholds and reset timeouts. The most common combinations are available as standard products, but the engineer can also specify threshold voltages from 2.5V to 5.0V in 100mV increments and minimum reset-delay times of 1ms, 20ms, 140ms, or 1.12s.
Woof!
Another common requirement for microprocessor-based systems is the watchdog timer (WDT). WDTs provide protection against rogue software and other aberrations that cause software execution to "run off into the weeds." The WDT is simply a restartable timer whose output (Active-low WDO) changes state on timeout, resetting the µP or generating an interrupt. To prevent the WDT from timing out, you connect an I/O line from the µP to the WDT input (WDI). Then, software must produce transitions on this line that repeatedly restart the watchdog before timeout. Otherwise, the WDO triggers an interrupt or reset.But My Microprocessor Has a Watchdog Function
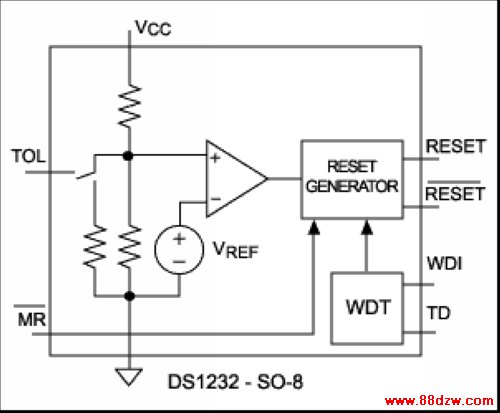
Many µPs have internal watchdog timers, but many of these WDTs do not provide complete protection. Often the WDT can be disabled as well as enabled by software. If software can disable the WDT, then the WDT cannot completely protect the system from software. To remove this liability, you need an external hardware watchdog timer that cannot be disabled by software.Many parts have this function, including the ubiquitous DS1232 from Dallas Semiconductor; it is one of the most duplicated supervisory circuits on the market (Figure 4a). This part provides the same functionality as four-terminal devices, plus a WDT that can be programmed via its TD pin for any of three different periods. Using the TOL pin, you can also set the threshold to one of two factory-set voltages. The '1232 also has complementary reset outputs. The original version was available only in eight-pin DIPs and the 16-pin wide-SO package. Newer versions are available in the eight-pin SO.
Most applications do not need the '1232's programmability or complementary outputs. Eliminating these features drops the pin count to five, allowing the remaining functionality to be implemented in a five-pin version of the SOT23. The first such parts available in a five-pin SOT23 are the MAX823 and MAX824 (Figure 4b). As with the '1232, their WDT output is internally gated with the power monitor output to provide a single Active-low RESET output. The MAX823 has an active-low Active-low RESET, and the MAX824 has an active-high RESET.
 |
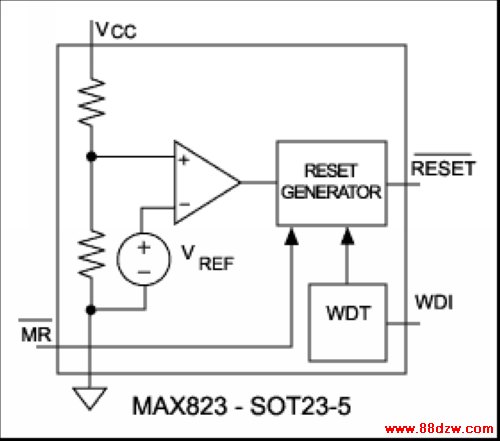 |
| Figure 4a. | Figure 4b. |
上一页 [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] 下一页
Tag:控制技术,计算机控制技术,工厂电气控制技术,控制技术
《检测电路保持您的微处理器控制-Supervisory Cir》相关文章
- › 恒流源供电和摘机检测电路图
- › 低功耗窗口温度检测电路图
- › 过零检测电路图
- › 电压输出式角度检测电路图
- › 电压检测电路图
- › 遥控红外检测电路图
- 在百度中搜索相关文章:检测电路保持您的微处理器控制-Supervisory Cir
- 在谷歌中搜索相关文章:检测电路保持您的微处理器控制-Supervisory Cir
- 在soso中搜索相关文章:检测电路保持您的微处理器控制-Supervisory Cir
- 在搜狗中搜索相关文章:检测电路保持您的微处理器控制-Supervisory Cir
分类导航
最新更新




 当前位置:
当前位置: