检测电路保持您的微处理器控制-Supervisory Cir
[09-13 17:05:09] 来源:http://www.88dzw.com 控制技术 阅读:8332次
文章摘要:Figure 4. These popular supervisory ICs include watchdog timers and a manual-reset input.As with the three- and four-terminal devices, these first five-pin SOT devices have spawned a family of parts that provide greater variation and flexibility for the designer. MAX6316 through MAX6322 devices, for
检测电路保持您的微处理器控制-Supervisory Cir,标签:计算机控制技术,工厂电气控制技术,http://www.88dzw.comFigure 4. These popular supervisory ICs include watchdog timers and a manual-reset input.
As with the three- and four-terminal devices, these first five-pin SOT devices have spawned a family of parts that provide greater variation and flexibility for the designer. MAX6316 through MAX6322 devices, for example, provide a variety of feature combinations and output structures in the SOT23-5. Available versions of these products offer reset thresholds in 100mV increments between 2.5V and 5.0V, four different minimum reset timeouts (1ms, 20ms, 140ms, or 1.12s), and four different minimum WDT timeout periods (4.3ms, 71ms, 1.12s, or 17.9s).
Monitoring Multiple Voltages with a Single Chip
Many systems require multiple supply voltages for operation. These voltages can be monitored with multiple devices, but most designers prefer a single device to monitor two or more voltages. The Dallas DS1834, for instance, monitors a 5V supply and a 3V or 3.3V supply.Systems that include both analog and digital circuitry often require that you monitor a digital supply voltage along with positive and negative analog supply voltages simultaneously. A MAX6304, MAX6307, or MAX6310 (available in SOT packages), plus four external resistors can do this job. The ICs differ only in the structure of their reset outputs: low-true open-drain, low-true push-pull, or high-true push-pull. They monitor voltages at the VCC pin using factory-preset reset thresholds that range from 2.5V to 5.0V in 100mV steps. Each device includes externally set undervoltage and overvoltage comparators whose thresholds are set by external voltage dividers. The under- and overvoltage inputs for these two comparators can implement a windowed reset function that gives warning (by generating a reset) when a particular voltage is either too high or too low.
Alternatively, you can use the overvoltage input as an undervoltage detector for a negative voltage. Combining this function with the preset and configurable undervoltage detector enables the chip to monitor a logic voltage such as 5V along with positive and negative analog voltages such as ±12V (Figure 5). The device shown has a low-true push-pull reset output (6310 base number), a nominal 4.63V preset threshold ('46' suffix), and a nominal 200ms reset timeout (D3 suffix). The external resistors shown generate resets when the analog voltages are less than ±10V.
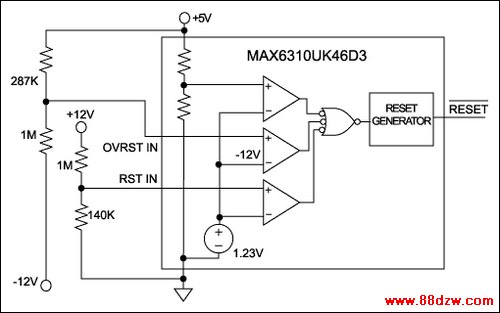
Figure 5. Internal comparators implement undervoltage/overvoltage warnings and windowed-reset functions.
To ensure the continuity of SRAM contents and other critical functions when supply voltage is lost, many of the older supervisory circuits are able (concurrently with reset) to switch the power source applied to such subsystems from the system supply to a backup battery. The need for this battery-backup switchover is in decline with the advent of flash memory, but it still exists in many systems. Most of the older supervisor chips have internal switches for the battery and the system supply, and for larger loads they can also switch the system supply by driving an external transistor.
上一页 [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] 下一页
Tag:控制技术,计算机控制技术,工厂电气控制技术,控制技术
《检测电路保持您的微处理器控制-Supervisory Cir》相关文章
- › 恒流源供电和摘机检测电路图
- › 低功耗窗口温度检测电路图
- › 过零检测电路图
- › 电压输出式角度检测电路图
- › 电压检测电路图
- › 遥控红外检测电路图
- 在百度中搜索相关文章:检测电路保持您的微处理器控制-Supervisory Cir
- 在谷歌中搜索相关文章:检测电路保持您的微处理器控制-Supervisory Cir
- 在soso中搜索相关文章:检测电路保持您的微处理器控制-Supervisory Cir
- 在搜狗中搜索相关文章:检测电路保持您的微处理器控制-Supervisory Cir
分类导航
最新更新




 当前位置:
当前位置: